Critical Flaws Discovered in Azure App That Microsoft Secretly Installs on Linux VMs
Introduction
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service from Microsoft. Azure offers a range of software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) options for deploying applications and services on Microsoft-managed data center infrastructure.
The Azure cloud platform has more than 200 products and cloud services designed to help to bring new solutions to life—to solve today’s challenges and create the future. Build, run and manage applications across multiple clouds, on-premises and at the edge, with the tools and frameworks of choice.
Microsoft has addressed four critical vulnerabilities collectively known as OMIGOD, found in the Open Management Infrastructure (OMI) software agent silently installed on Azure Linux machines accounting for more than half of Azure instances.
Azure cloud customers and elevate privileges as well as allow for remote takeover of vulnerable systems.
OMI
Open Management Infrastructure (OMI) is an open-source analogous equivalent of Windows Management Infrastructure (WMI) but designed for Linux and UNIX systems such as CentOS, Debian, Oracle Linux, Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server, SUSE Linux, and Ubuntu that allows for monitoring, inventory management, and syncing configurations across IT environments.
Millions of endpoints exposed to attacks
The researchers “conservatively estimate” that thousands of Azure customers and millions of endpoints are impacted by these security flaws:
- CVE-2021-38647 – Unauthenticated RCE as root (Severity: 9.8/10)
- CVE-2021-38648 – Privilege Escalation vulnerability (Severity: 7.8/10)
- CVE-2021-38645 – Privilege Escalation vulnerability (Severity: 7.8/10)
- CVE-2021-38649 – Privilege Escalation vulnerability (Severity: 7.0/10)
Tools or Services are at risk
All Azure customers with Linux machines running one of the following tools or services are at risk:
- Azure Automation
- Azure Automatic Update
- Azure Operations Management Suite (OMS)
- Azure Log Analytics
- Azure Configuration Management
- Azure Diagnostics
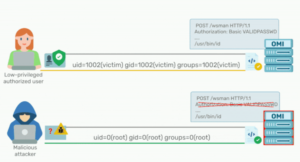
The most critical of the four flaws is a remote code execution flaw arising out of an internet-exposed HTTPS port like 5986, 5985, or 1270, allowing attackers to obtain initial access to a target Azure environment and subsequently move laterally within the network.
Recommendation
Microsoft has released patches for these four critical OMI vulnerabilities, there is no auto-update mechanism Microsoft can use to update the vulnerable agents on all Azure Linux machines, which means that customers have to upgrade it manually to secure endpoints from any incoming attacks using OMIGOD exploits.
If OMI listening on ports 5985, 5986, 1270 we advise limiting network access to those ports immediately in order to protect from the RCE vulnerability (CVE-2021-38647).
Try to not work with highest privileges (root) always work with low privileged users to protect form RCE and escalate privileges.
To manually update the OMI agent:
- To upgrade OMI platform’s package tool use the command (for example, sudo apt-get install omi or sudo yum install omi).
- It is recommended to download and install the OMI client v1.6.8.1 (Github) from the official vendor.



