Apache fixes zero-day vulnerability exploited in the wild, patch now
Introduction
The Apache HTTP Server, colloquially called Apache, is a free and open-source cross-platform web server software, released under the terms of Apache License 2.0.
As a Web server, Apache is responsible for accepting directory (HTTP) requests from Internet users and sending them their desired information in the form of files and Web pages. Many of the Web’s software and code is designed to work along with Apache’s features.
The Apache Software Foundation has released version 2.4.50 of the HTTP Web Server to address two vulnerabilities, one of which is an actively exploited path traversal and file disclosure flaw.
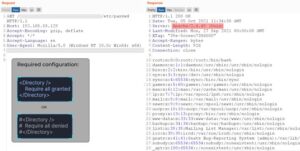
Path traversal attacks involve sending requests to access backend or sensitive server directories that should be out of reach. Normally, these requests are blocked, but in this case, the filters are bypassed by using encoded characters (ASCII) for the URLs.
Impact
An attacker could use a path traversal attack to map URLs to files outside the expected document root
A null pointer dereference detected during HTTP/2 request processing. This flaw allows an attacker to perform a denial of service (DoS) attack on the server.
CVE Tracked as
1) CVE-2021-41524 :- null pointer dereference in h2 fuzzing
2) CVE-2021-41773 :- Path traversal and file disclosure vulnerability
Recommendation
All users should ensure that they update to the fixed version, 2.4.50. To download the updated Apache HTTP Server 2.4.50 Visit to https://httpd.apache.org/download.cgi
- Stay informed:- Stay tuned to the news and pay attention to releases from the software vendors, user may have time to put in security measures or respond to a threat before it gets exploited.
- Keep the system updated:- Make sure your software platforms are up to date at all times.
- Employ additional security measures:- Ensure that use security solutions that protect against zero day attack because these security measures may not be enough to fully protect from a zero day attack.



