VirusTotal Releases Ransomware Report Based on Analysis of 80 Million Samples
Introduction
Ransomware is a form of malware that cyber criminals use to encrypt the victim’s file then demand a payment – often in Bitcoin – in exchange for the decryption key. Ransom demands can reach millions of dollars.
Experts suggest that a ransomware attack may occur as often as every 11 seconds in 2021. US government agencies report that an average of 4,000 ransomware attacks have occurred per day across the past five years. Ransomware attacks have increased by more than 150% by volume, year-over-year, according to one report.
Report by VirusTotal
In 2020 and early 2021, 130 different ransomware families were found to be active, with Israel, South Korea, Vietnam, China, Singapore, India, Kazakhstan, the Philippines, Iran and the United Kingdom being the most affected. The territory reveals a comprehensive analysis of 80 million ransomware-related samples.
Google’s cybersecurity arm VirusTotal attributed a significant chunk of the activity to the GandCrab ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) group (78.5%), followed by Babuk (7.61%), Cerber (3.11%), Matsnu (2.63%), Wannacry (2.41%), Congur (1.52%), Locky (1.29%), Teslacrypt (1.12%), Rkor (1.11%), and Reveon (0.70%).
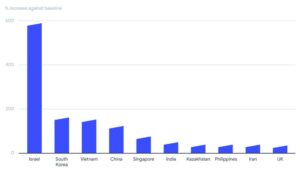
Israel, South Korea, Vietnam, China, Singapore, India, Kazakhstan, Philippines, Iran and the UK were the 10 most affected territories based on the number of submissions reviewed by VirusTotal.
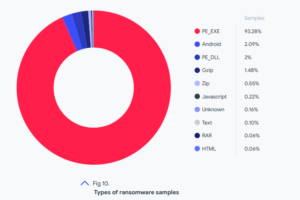
Some of the other important points revealed in this study are:
- GandCrab accounted for the majority of ransomware activity in the first two quarters of 2020, with the Babuk ransomware family causing a surge in infection in July 2021.
- 95% of the detected ransomware files were Windows-based executables or dynamic link libraries (DLLs), and 2% were Android-based.
- Approximately 5% of the samples analyzed were related to Windows privilege escalation, SMB information disclosure, and exploits related to remote execution.
- Emotet, Zbot, Dridex, Gozi, and Danabot were the leading malware artifacts used to distribute ransomware.
Remediation To Prevent Ransomware
1) Isolation:- Prevent the infection from spreading by disconnecting the network cable, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and all external storage devices such as USB or external hard drives.
2) Ensure backups have not been compromised:- Just check that the backup system not infected by ransomware. Backup data should never be available in read/write mode.
3) Identification:- Investigate the type of ransomware you’re facing, how it entered your system, and how it spreads in order to seal the breach.
4) Try to remove the malware or recover from backup:- It is questionable whether or not you can successfully remove an infection. A strong backup strategy should allow you to restore from the most recent clean backup to avoid paying the ransom.
5) Engage your incident response team:- Notify the appropriate stakeholders to activate your business continuity plan.
6) Diagnose the scope of infection:- Quickly identify which files have been impacted and where they are located.
7) Recover quickly:- Restore your files to the most recent clean version of impacted data.
8) Alert the authorities:- Inform law enforcement, customers, and any other necessary authorities. This is highly dependent on your business and industry



