Microsoft warns of ongoing supply chain attacks by the Nobelium hacker group
Introduction
A supply chain attack is a type of cyber attack that target’s organizations by focusing on weaker links in an organization’s supply chain. By targeting a weak point in a supply chain, a cyber attack may be more likely to succeed with attackers taking advantage of the trust that organizations may have in third-party vendors.
Nobelium hacker group
A Russia-based group called Nobelium has been linked to the massive 2020 SolarWinds hack that compromised about 100 U.S. companies — including Microsoft, Intel and Cisco — in addition to a dozen government agencies including the Treasury, Justice and Energy departments and the Pentagon.
Nobelium has been attempting to replicate the approach it has used in past attacks by targeting organizations integral to the global IT supply chain
What Happened
Nobelium, the threat actor behind the SolarWinds compromise in December 2020, has been behind a new wave of attacks that compromised 14 downstream customers of multiple cloud service providers (CSP), managed service providers (MSP), and other IT services organizations, illustrating the adversary’s continuing interest in targeting the supply chain via the “compromise-one-to-compromise-many” approach.
Microsoft’s corporate vice president of customer security and trust, Burt said these activities further underscore Russia’s continued attempts to infiltrate the supply chain. This time, Nobelium has been attacking a different part of the supply chain: resellers and other technology service providers that customize, deploy and manage cloud services and other technologies.
Microsoft, which disclosed details of the campaign on Monday, said it had notified more than 140 resellers and technology service providers that have been targeted by Nobelium. Nobelium selected 609 customers and is said to have been attacked a total of 22,868 times.
Impact
Nobelium ultimately wants resellers to piggyback on direct access to their customers’ IT systems and impersonate their organization’s trusted technology partners to give them access to downstream customers.
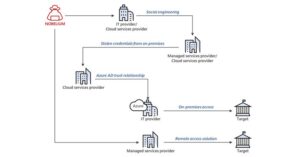
The newly disclosed attacks do not exploit certain security weaknesses in the software, rather than exploiting them. Lever action Various techniques, such as password spraying, token theft, API abuse, and spear phishing to steal credentials associated with service provider privileged accounts, allow attackers to move sideways in a cloud environment and even break into it.
Recommendations
1) Deploy strong code integrity policies to allow only authorized apps to run.
2) Use endpoint detection and response solutions that can automatically detect and remediate suspicious activities.
3) Maintain a highly secure build and update infrastructure.
4) Build secure software updaters as part of the software development lifecycle.
5) Develop an incident response process for supply chain attacks.
6) It is recommended that organization’s enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) and delegated administrative privilege (DAP) audits to prevent potential misuse of elevated privileges.



