Malicious Python packages caught stealing Discord Tokens, Installing Shells
The Operators of the Python Package Index (PyPI) have uncovered as many as 11 malicious Python packages that have been cumulatively downloaded more than 41,000 times. And could be exploited to steal Discord access tokens, passwords, and even stage dependency confusion attacks.
The Python packages have since been removed are the following responsible disclosure by DevOps firm JFrog —
- important package / important-package
- pptest
- ipboards
- owlmoon
- DiscordSafety
- trrfab
- 10Cent10 / 10Cent11
- yandex-yt
- yiffparty
These “important package,” “10Cent10” were found obtaining a reverse shell on a compromised machine, giving the attacker full control over the system. And the two other packages “ipboards” and “trrfab” masqueraded as legitimate dependencies designed to be automatically imported by taking advantage of a technique called dependency confusion or namespace confusion.
Where a malicious actor deliberately publishes packages with misspelled names of popular variants, dependency confusion works by uploading to public repositories a number of poisoned components with names that are the same as the legitimate internal private packages, but with a higher version, effectively forcing the target’s package manager to download and install the malicious module.
The dependency “importantpackage” also stands out for its novel exfiltration mechanism to evade network-based detection, which involves using Fastly’s content delivery network (CDN) to mask its communications with the attacker-controlled server as communication with pypi[.]org.
JFrog researchers Andrey Polkovnychenko and Shachar Menashe explained that the malicious code “causes an HTTPS request to be sent to pypi.python[.]org (which is indistinguishable from a legitimate request to PyPI), which later gets rerouted by the CDN as an HTTP request to the [command-and-control] server.”
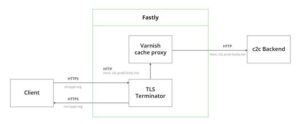
Lastly, both “ipboards” and a fifth package named “pptest” were discovered using DNS tunneling as a data exfiltration method by relying on DNS requests as a channel for communication between the victim machine and the remote server. JFrog said it’s the first time the technique has been spotted in malware uploaded to PyPI.
Efforts to target popular code registries like Node Package Manager (NPM) JavaScript registry, PyPI, and RubyGems have become commonplace and a new frontier for an array of attacks.
Menashe, JFrog’s senior director of research once said “Package managers are a growing and powerful vector for the unintentional installation of malicious code, and the attackers are getting more sophisticated in their approach”. “The advanced evasion techniques used in these malware packages, such as novel exfiltration or even DNS tunneling signal a disturbing trend that attackers are becoming stealthier in their attacks on open-source software.”
GitHub earlier this week outlined plans to tighten the security of the NPM registry by requiring two-factor authentication (2FA) for maintainers and admins starting in the first quarter of 2022. After at least three NPM developer accounts were compromised by bad actors to insert malicious code into popular packages “ua-parser-js,” “coa,” and “rc”.
Remediation:
The remediation action that can be taken into consideration:
- Python Package Index (PyPI) are the important features of the Python and always update the Python Package Index (PyPI).
- Discord tokens can be revoked
- SSH keys can be changed



