EVILNUM MALWARE
Hackers using are targeting financial and investment firms in an ongoing operation of the Evilnum malware which is a known backdoor that may be exploited to steal data or load other payloads.
The threat actor responsible for the activity, identified by Proofpoint researchers as TA4563, targeted Decentralized Finance (DeFi) enterprises and businesses in Europe with activities supporting currency exchanges and cryptocurrencies. The campaign, which coincides with that of the well-known Evilnum APT (also known as DeathStalker) activity, was first noticed in late 2021 and is still running strong today.
According to an analysis released on Thursday by Proofpoint researchers Bryan Campbell, Pim Trouerbach, and Selena Larson, “The identified campaigns delivered an updated version of the Evilnum backdoor using a varied mix of ISO, Microsoft Word and Shortcut (LNK) files in late 2021 and early 2022, presumably as a method of testing the efficacy of the delivery methods. This malware can be used for reconnaissance, data theft, and to deploy additional payloads.”
WORKING
Spear phishing emails are used to contact targets, they provide a link to a ZIP file stored on Google Drive. Multiple LNK (also known as a shortcut) files found in that archive unpack and run malicious JavaScript code while displaying a fake page. The “double extensions” on these shortcut files are an attempt to deceive the user into opening them, believing they are innocent documents or images (in Windows, file extensions for known file types are hidden by default). Below is a screenshot of one of the ZIP files’ contents.
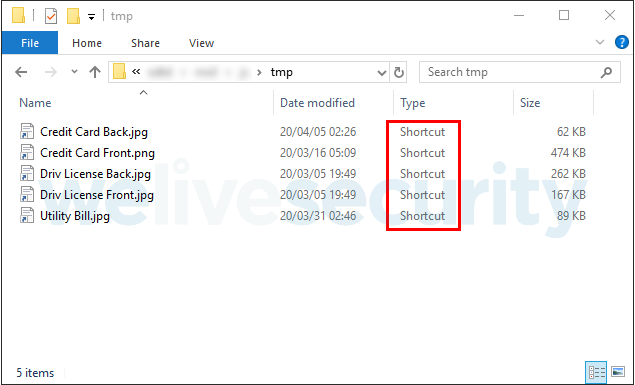
No matter which shortcut file is accessed, it will perform the same action. it will search the contents of its file for lines that contain a particular marker and write those lines to the a.js file. The malicious JavaScript file is then executed, writing and opening a fake file with the same name as the shortcut but with the right extension. In addition, the shortcut file is removed. The majority of the documents used as ruses are images of credit cards, identification documents, or utility bills with proof of residence, as many financial institutions are required by law (“Know Your Customer”) to request these documents from new customers.
It is believed that this group has gathered these fake documents over many years of operation since they appear to be real. As it targets technical support agents and account managers, who frequently get these kinds of documents from their clients, documents are actively collected in the group’s current operations. Except when the targets come from different geographical areas, the organization reuses the documents on several targets.
The first stage of the attack is a JavaScript component that can distribute more malware, such as a C# spy component, Golden Chickens components, or various Python-based tools. Other researchers previously referred to the C# component as Evilnum, but the JS component has also been called Evilnum. As their main piece of malware goes by the name Evilnum, it is given the organization that same name, and it will be called the individual malware components.
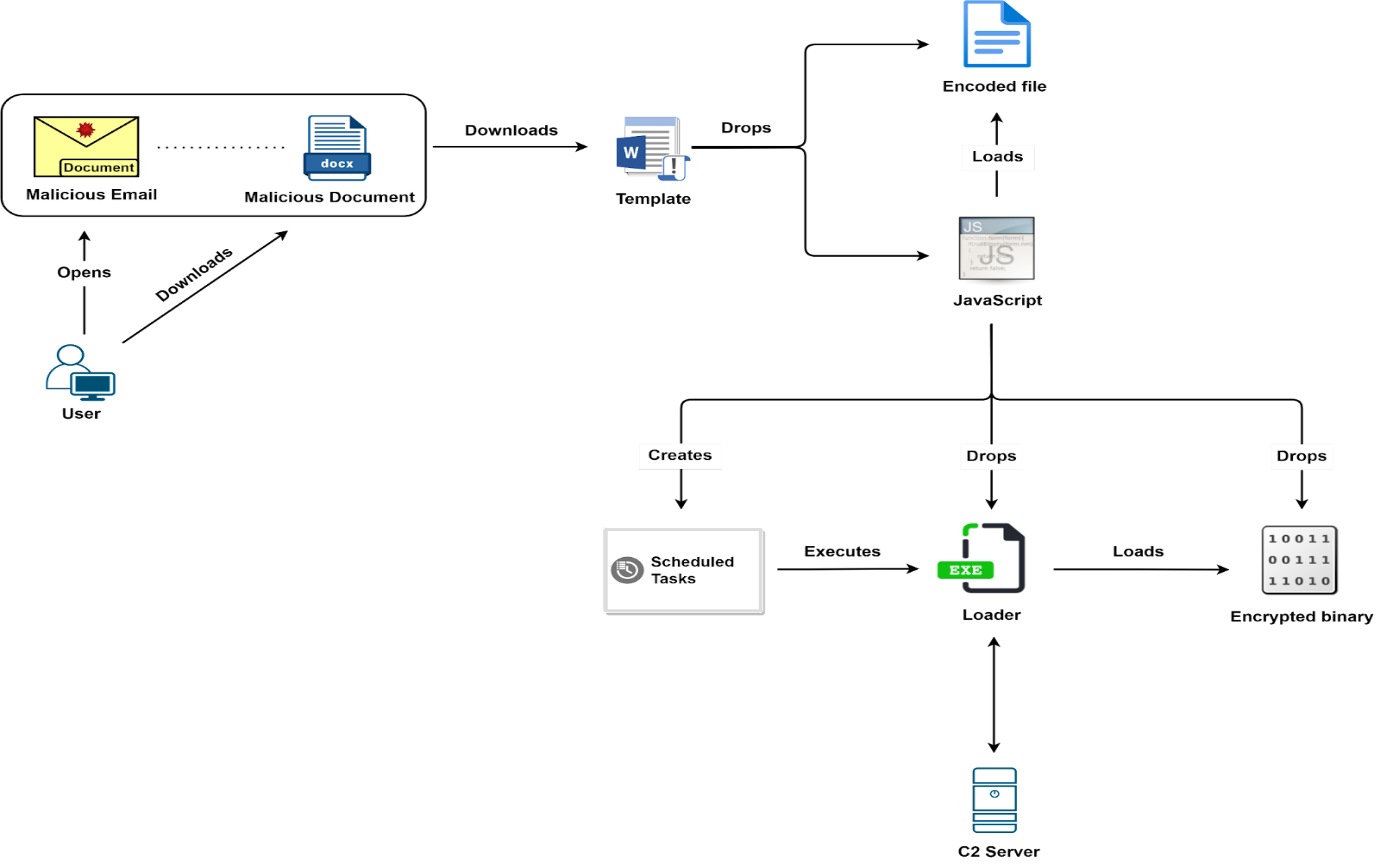
Every one of the different components has its C&C server and functions separately. The malware’s creators manually transmit commands to install more components and, if they deem it necessary, utilize post-compromise programmes and tools.
The majority of servers that the malware uses are referred to via IP addresses rather than domain names. The C&C servers utilized by the Golden Chickens components and malware purchased from a MaaS supplier, which we discuss later, are the sole exceptions.
According to the host, those identified by an IP address can be divided into two groups. A Ukrainian service named FreeHost hosts the majority of them. The remainder is hosted by Dotsi in the Netherlands.
REMEDIATIONS
The users can prevent themselves from the attack of Evilnum Malware by the following remedies –
- Do not permit government spying
Users should be aware of the problems the government has with monitoring citizen behavior and collecting user data, and users should educate themselves on shady information collection techniques. By remaining completely anonymous online, one can prevent any unwanted government tracking or spying.
When the user goes online, they can select a different location and view whatever content they want without any specific content limitations. By using a Private Online Access VPN, they may simply enjoy an internet connection without running the danger of being hacked.
Users can surf the web without being watched if they manage the information that the government or other third parties can access. Even if they do not engage in criminal activity or have confidence in the platforms or services they choose, be wary of the security and take precautions by using a VPN service.
- Backup of the files, in the event of a malware attack
Data loss can happen to computer users as a result of cyber viruses or their careless actions. Unexpected power outages could result in the loss of crucial information, while ransomware can encrypt and keep files hostage. If users have accurate, current backups, they can quickly recover from such an occurrence and resume working. To ensure that the most recent data is preserved, it is equally necessary to regularly update backups, they may enable this process to be carried out automatically.
Users can avoid annoyance and breakdowns by keeping the prior version of any critical document or project. When malware appears out of nowhere, it is useful. To restore the data, use Data Recovery Pro.



