NSA Releases Guide to Combat Powerful Black Lotus Bootkit Targeting Windows Systems
U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) has released some preventive measures to help the organizations in protecting their systems from BlackLotus.
BlackLotus is type of a bootkit or a modern malware that was found in Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI).
The BlackLotus has the capability of bypassing the security measures of the windows booting process.
UEFI:
UEFI stands for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface is a modern firmware interface that acts like a connective link or a bridge between the computer’s operating system (OS) and its hardware system.
Earlier in the traditional computers, Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) was used for starting up of the computer. But nowadays, it is replaced by the UEFI.
As compared to the traditional BIOS, the UEFI is much standardized and prove more features in its interface for initializing and managing the hardware components of a computer system during its booting process.
Advantages of UEFI are: –
- UEFI interface performs the initializing process of the hardware components of a computer in a parallel manner, which makes the booting process faster as compared to BIOS that initializes the components in a sequential manner.
- UEFI provides enhanced security feature by protecting the booting process against the malware attacks and unauthorized changes. UEFI does this by verifying the digital signatures of the firmware devices, bootloader and the operating system (OS)
- UEFI provides larger disk capacities and more disk partitions than the Master Boot Record (MBR). It uses the GPT partitioning scheme which provides 128 partitions as compared to MBR which provides only 4 partitions.
- UEFI is designed to be much flexible and adjustable as compared to MBR. The manufacturers can easily add new features and support for advanced hardware components. This makes UEFI much compatible with the modern-day hardware technologies and devices.
- UEFI provides an attractive and a user-friendly Graphical User Interface (GUI) as compared to the text-based GUI of BIOS.
- UEFI provides advanced networking features such as network booting, firmware updates, pre-boot network configurations for the remote management of the systems.
BlackLotus:
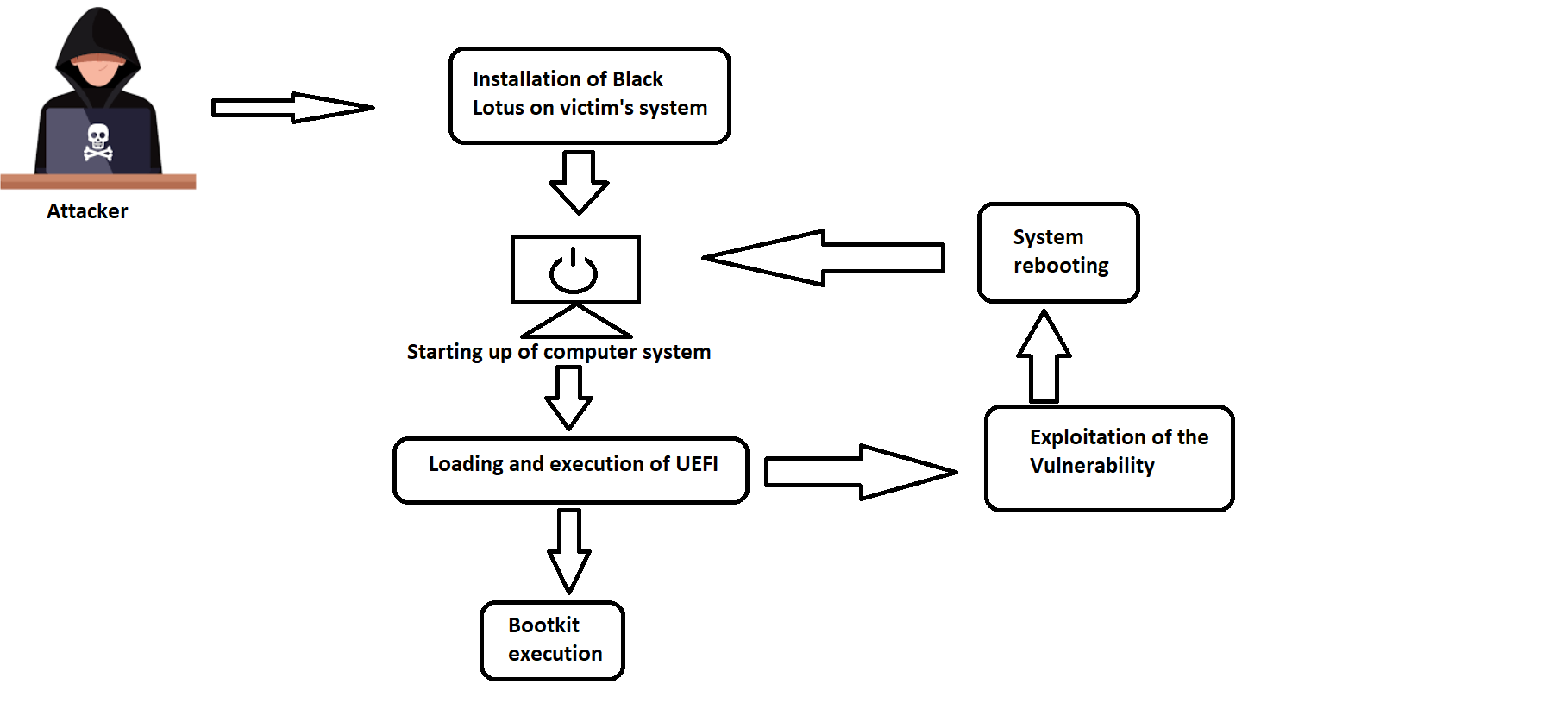
BlackLotus is a Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) bootkit. BlackLotus is basically a type of a malware or a malicious software which targets the UEFI which is nowadays used in place of the BIOS for the booting process while starting up the computer.
BlackLotus takes over the control over the computer system just before the starting of the booting process. It operates at a lower level and directly attacks the UEFI firmware by manipulating it.
BlackLotus attacks a computer system by exploiting its vulnerabilities and weak points like manipulative code injection, privilege escalation or buffer overflow, which allows it to inject its malicious and manipulative code into the UEFI firmware.
This malicious code helps the attacker in intercepting and controlling the booting process, due to which the bootkit gets loaded before the operating system and the security systems are unable to detect it. This allows the attacker to acquire control of the operating system at early stages.
This malicious code affects the sensitive functions and components of the booting process, like the bootloader or kernel. The BlackLotus bootkit can redirect bypass the security systems and redirect system calls by gaining complete control over the booting process and the operating system.
After gaining full control over the operating system, the bootkit can easily hide its presence and activities from getting detected by the security systems.
It makes changes to the behavior of the operating system, modifies the main structure of the system and can damage the memory to save itself from getting detected.
The BlackLotus bootkit creates a backdoor communication link to provide unauthorized access to the attackers, to carry on further exploitation and malicious activities inside the system.
Preventive Measures:
- Update the system with the latest security patches and firmware updates to tackle the current vulnerabilities.
- Customize the UEFI Secure Boot to block older (pre-January 2022), signed Windows boot loaders.
- Configure the security software like endpoint security software to prevent the BlackLotus malware from installing in the system.
- The firmware updates and safety patches must be from secure and trusted sources to prevent any type of malicious codes to enter into the system.
- Use security devices such as firewalls and Intrusion Detection System (IDS) to prevent any type of network traffic from unsafe sources from entering into the system.
- Download any software, application or file from secure and official sources and avoid clicking on the suspicious links.
- Regular scanning and monitoring of the system must be done to check for the presence of any suspicious modifications to the critical or sensitive components.



