SiegedSec Allegedly Breached NATO’s COI Portal Affecting 31 Nations Leaked Sensitive Data
NATO recently confirmed of a data security theft. Being such an important organisation it holds a lot of valuable information. It thus can be disastrous if any unwanted information gets into the hands of criminal gangs etc.
The IT team is currently looking into reports of a possible data breach on the Communities of Interest (COI) Cooperation Portal by a hacker group called SiegedSec. The COI Cooperation Portal, located at dnbl.ncia.nato.int, serves as NATO’s unclassified platform for sharing information and fostering collaboration among NATO organizations and member countries.
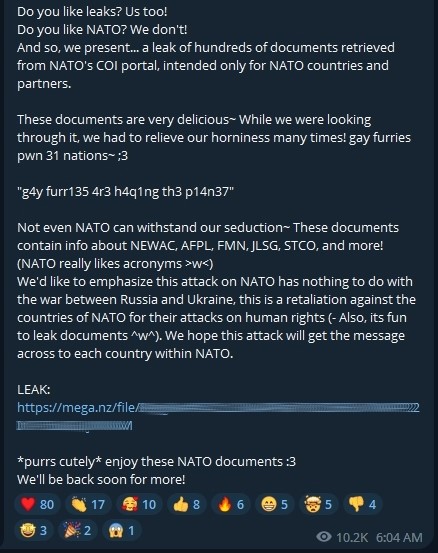
This was posted by the hacker group on telegram. They were seen challenging NATO and boasting about having leaked a lot of their data.
Affected Software
On 24 July 2023, CloudSEK’s contextual AI digital risk platform XVigil discovered a Telegram post where a highly reputed threat actor group disclosed the data breach of the COI (Communities of Interests) Cooperation Portal, NATO’s unclassified information-sharing and collaboration environment. The portal supports NATO organizations, NATO Nations, and their mission partners’ public administration.
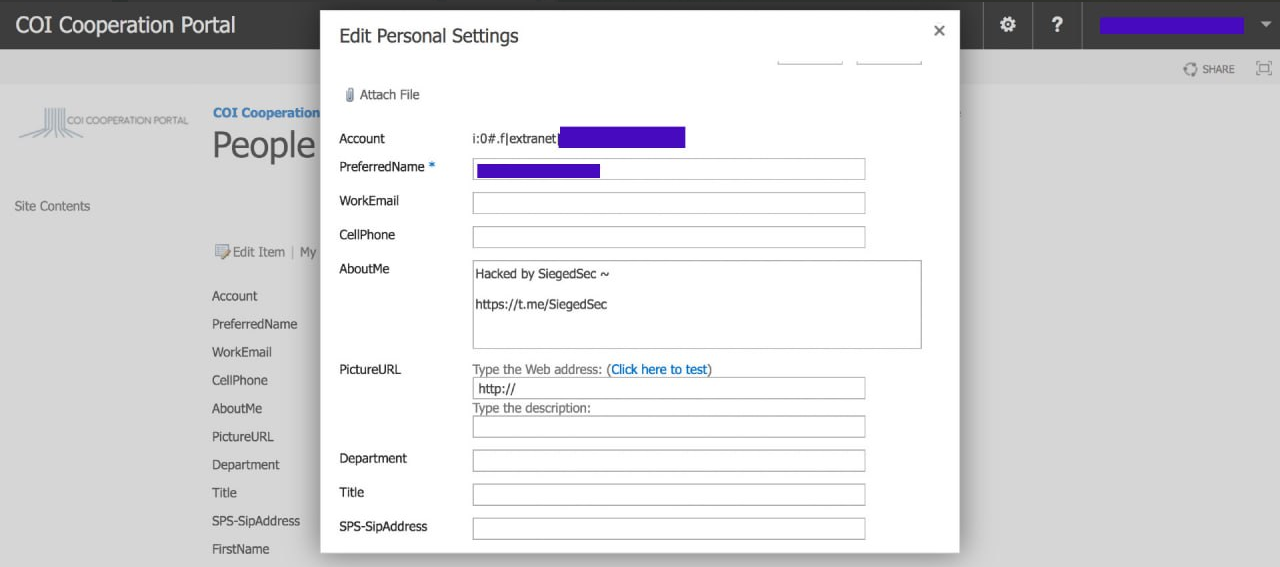
The above image is a representation of the portal used my NATO to share classified documents. This software was injected with malware by SiegedSec.
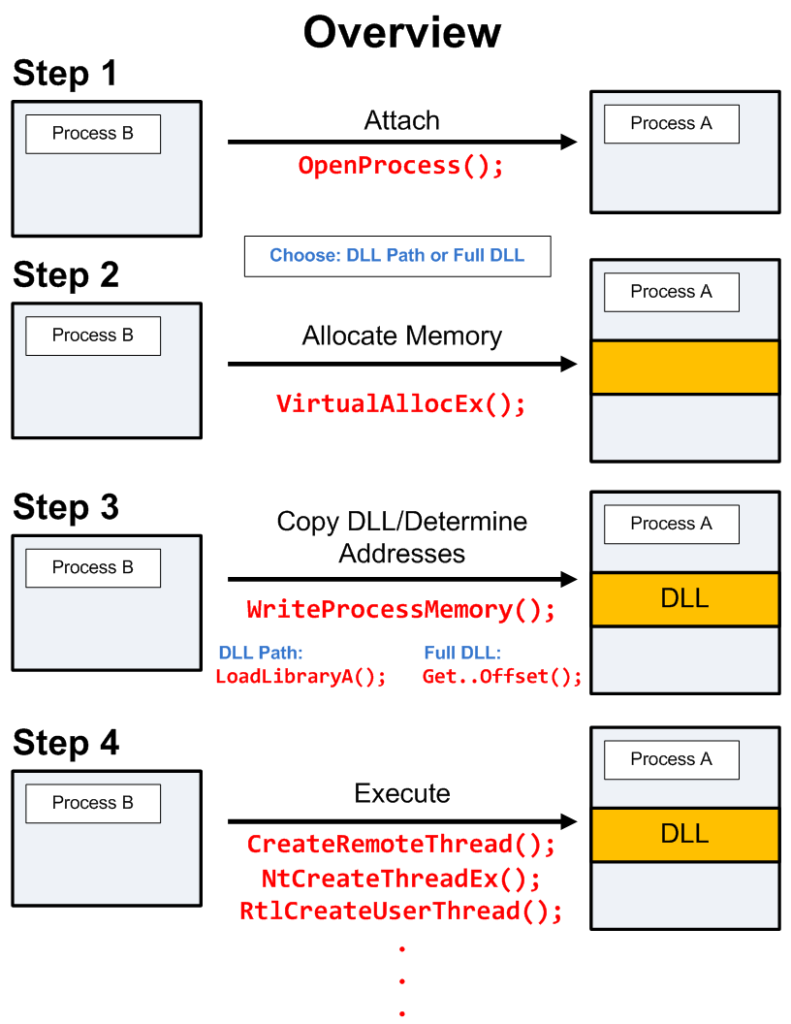
The above image is an example of malware injection. This showcases how malware injection can be performed in a stepwise manner. This was injected into the software and then a huge amount of data was stolen from the software.
Impact
Cybersecurity company CloudSEK assisted NATO in investigating the data theft. The data theft comprised of 845 MB of files, 8000 rows of user’s sensitive information. The method is used for extracting data is malware injection.
According to CloudSEK’s study, there are signs that the alleged data leak may have consequences for 31 NATO member countries. In response to inquiries about the legitimacy of the leaked material, a NATO official said that they are taking the claims seriously and have started a full inquiry into the purported occurrence. At dnbl.ncia.nato.int, the Communities of Interest (COI) Cooperation Portal serves as a vital forum for exchanging unclassified information and promoting cooperation among NATO member countries and organisations. NATO is actively trying to determine the veracity and size of the purported data leak as events evolve. Concerns about potential data breaches have been raised by the cyber security attack, which is blamed on the hacker collective SiegedSec.
Mitigation
Malware injection is the root cause of this data theft in this NATO website. Preventing malware injection is crucial for maintaining the security of systems and data. Here are five effective measures to help mitigate the risk of malware injection:
Regular Software Updates and Patching: Keep all software, operating systems, and applications up to date with the latest security patches. Cybercriminals often exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software to inject malware.
Use Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): Implement a WAF to inspect and filter incoming web traffic, detecting and blocking malicious attempts to inject malware into web applications.
Secure Coding Practices: Promote secure coding practices during the development process to minimize vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit to inject malware. Regularly conduct security code reviews and utilize automated security testing tools to identify potential weaknesses.
Content Security Policy (CSP): Implement a robust CSP for web applications, specifying which sources of content are allowed to be loaded, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized scripts or malicious content injection.
Employee Awareness and Training: Educate employees and system users about the risks associated with malware injection. Teach them to recognize phishing attempts and suspicious links and to avoid downloading files from untrusted sources.
By adopting these preventive measures and maintaining a proactive approach to cybersecurity, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood of malware injection and enhance their overall security posture.



