Iranian Cyber Espionage: Targeting Middle East Policy Experts with the New BASICSTAR Backdoor
Charming Kitten, identified as a notorious threat actor of Iranian origin, has come under scrutiny for its involvement in a string of cyberattacks directed at Middle East policy experts. This blog aims to offer comprehensive insights into the tactics employed by this group and proposes actionable steps for enhancing cybersecurity defenses. By delving into the intricacies of Charming Kitten’s modus operandi and providing detailed remediation strategies, organizations can bolster their resilience against the sophisticated cyber threats posed by this group.
Understanding Charming Kitten
Charming Kitten, known by various aliases such as APT35, CharmingCypress, Mint Sandstorm, TA453, and Yellow Garuda, employs sophisticated social engineering tactics to target a range of organizations including think tanks, NGOs, and journalists. Their modus operandi involves engaging targets in prolonged email exchanges, making it challenging to detect their activities. Recent cyberattacks, particularly targeting Middle East policy experts, have highlighted their adeptness in utilizing advanced techniques. This technical analysis endeavors to delve into the intricacies of their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of their highly sophisticated operations.
Recent Attacks and Tactics
In recent cyber offensives orchestrated by Charming Kitten, a new backdoor known as BASICSTAR has been weaponized and propagated through deceptive channels, notably fake webinar portals. Employing sophisticated phishing tactics, the threat actor masquerades as reputable entities such as the Rasanah International Institute for Iranian Studies (IIIS), leveraging compromised email accounts and the deceptive technique of Multi-Persona Impersonation (MPI) to ensnare unsuspecting targets. The attack chain unfolds with the distribution of RAR archives harboring LNK files, acting as initial vectors for malware infiltration. Once executed, these malicious payloads, including BASICSTAR and KORKULOADER, facilitate unauthorized access and data exfiltration. Such intricate maneuvers underscore Charming Kitten’s evolving arsenal and strategic acumen in exploiting technological vulnerabilities and human susceptibility alike. These findings underscore the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures, including heightened vigilance against social engineering ploys and the implementation of advanced threat detection mechanisms, to mitigate the risks posed by Charming Kitten’s nefarious activities.
Social Engineering Tactics
Renowned for its extensive repertoire of social engineering campaigns, Charming Kitten consistently sets its sights on high-value targets such as think tanks, NGOs, and journalists. A hallmark of their modus operandi involves the artful cultivation of trust through protracted email interactions with their intended victims. Through these prolonged exchanges, Charming Kitten adeptly builds rapport, effectively lowering the target’s guard before ultimately delivering malicious content. This calculated approach underscores the group’s adeptness in exploiting human psychology and interpersonal dynamics to facilitate successful infiltration and compromise of their targets. By leveraging the element of trust, Charming Kitten amplifies the efficacy of their social engineering tactics, posing significant challenges for organizations seeking to defend against their nefarious activities. As such, it is imperative for entities to remain vigilant and implement robust cybersecurity measures to mitigate the risks posed by Charming Kitten’s sophisticated social engineering campaigns.
Malware Deployment
Charming Kitten employs an array of sophisticated malware tools as part of their strategy to compromise targets. Recent attacks orchestrated by the group have notably featured the utilization of MischiefTut, MediaPl (also known as EYEGLASS), BASICSTAR, among others. These malicious tools are designed with multifunctional capabilities, enabling them to harvest sensitive information and execute commands remotely on compromised systems. The deployment of such advanced malware underscores Charming Kitten’s technical proficiency and strategic adaptability in carrying out targeted cyber operations. By leveraging these tools, the group effectively breaches the security defenses of their targets, posing significant risks to the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive data. Organizations must remain vigilant and implement robust cybersecurity measures to detect and mitigate the threat posed by Charming Kitten’s arsenal of sophisticated malware tools.
Phishing Techniques
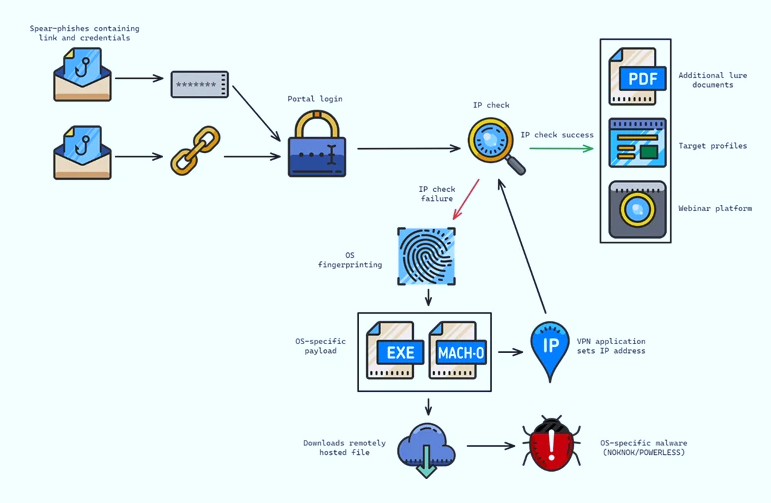
During the period spanning September to October 2023, Charming Kitten’s phishing campaigns were characterized by their adept impersonation of the Rasanah International Institute for Iranian Studies (IIIS) as a means to establish a facade of credibility and engender trust among their targets. Notably, these attacks were augmented by the exploitation of compromised email accounts and the strategic utilization of Multi-Persona Impersonation (MPI), amplifying their effectiveness in deceiving unsuspecting victims. By leveraging these sophisticated tactics, Charming Kitten effectively blurs the lines between authenticity and deception, heightening the susceptibility of their targets to falling prey to their malicious schemes. Such nuanced approaches underscore the group’s advanced capabilities in orchestrating targeted cyber operations and highlight the imperative for organizations to bolster their cybersecurity defenses through heightened awareness and robust threat mitigation strategies.
Infection Chain
The typical attack chain orchestrated by Charming Kitten commences with the distribution of RAR archives containing LNK files, serving as initial vectors for malware dissemination. Among the malicious payloads deployed is BASICSTAR, a Visual Basic Script (VBS) malware renowned for its multifaceted capabilities. This malicious script exhibits the capacity to gather comprehensive system information, execute commands remotely, and camouflage its activities through the downloading of decoy PDF files. Notably, Charming Kitten’s adaptability extends to tailoring their malware deployment based on the victim’s operating system. For Windows victims, the group deploys backdoors such as POWERLESS, while Apple macOS targets may find themselves compromised through infection chains culminating in the deployment of NokNok. This meticulous approach underscores Charming Kitten’s sophistication in orchestrating targeted cyber operations and emphasizes the critical importance of implementing robust cybersecurity measures to thwart their malicious endeavors effectively.
Targeting and Surveillance
Charming Kitten exhibits a profound commitment to conducting comprehensive surveillance on their targets, employing sophisticated methods to meticulously gather intelligence. This dedication extends to the strategic planning of manipulation tactics and the deployment of malware, distinguishing them from other threat actors in the cybersecurity landscape. Their unwavering persistence in perpetrating ongoing campaigns underscores their operational agility and underscores the importance of continuous vigilance in defending against their clandestine activities. Such relentless efforts highlight the need for organizations to adopt proactive measures and robust cybersecurity strategies to mitigate the evolving threat posed by Charming Kitten and safeguard against potential vulnerabilities in their networks.
Affiliation with IRGC
The group, believed to have ties to Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), has been implicated in targeting Western nations, as uncovered by Recorded Future. This nefarious activity is facilitated through a network of contracting companies specializing in surveillance and offensive technologies. Recorded Future’s revelations shed light on the intricate web of entities involved in these operations, highlighting the sophisticated nature of the group’s tactics and the extent of their global reach. Such findings underscore the urgent need for heightened vigilance and international cooperation in countering the threat posed by these state-affiliated actors and their clandestine networks.
Remediation Steps
- User Awareness Training: Educate users about the dangers of phishing emails and social engineering tactics. Encourage skepticism and provide guidance on identifying suspicious emails.
- Email Security Measures: Implement robust email security solutions to detect and block phishing attempts. Use advanced threat protection features to identify malicious attachments and URLs.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enforce MFA for all user accounts to add an extra layer of security against unauthorized access, even if credentials are compromised.
- Patch Management: Keep software and operating systems up to date with the latest security patches to mitigate vulnerabilities exploited by malware like BASICSTAR and KORKULOADER.
- Network Segmentation: Segment network resources to limit the lateral movement of malware within the network. Implement strict access controls and firewall rules to prevent unauthorized access.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Deploy EDR solutions to monitor and respond to suspicious activities on endpoints. Leverage advanced threat hunting capabilities to identify and mitigate threats.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to ensure a swift and effective response to cyberattacks. Define roles and responsibilities, establish communication channels, and outline procedures for containing and eradicating threats.



