Targeting Latin America and Europe: Banking Trojans Exploit Google Cloud Run
In recent times, cybersecurity experts have noted a troubling uptick in email phishing endeavors employing sophisticated methodologies to disseminate banking trojans and extract confidential data. These campaigns leverage Google Cloud Run, a managed compute platform, as a strategic tool for deploying malicious infrastructure with remarkable efficiency. Moreover, threat actors have embraced QR code attacks as part of their arsenal, circumventing conventional security protocols and presenting formidable obstacles for cybersecurity practitioners globally. This surge in phishing activities underscores the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, necessitating heightened vigilance and innovative defense strategies from cybersecurity professionals. As attackers continuously adapt their tactics to exploit emerging technologies and vulnerabilities, organizations must remain proactive in fortifying their defenses and mitigating the risks posed by such sophisticated cyber attacks. Effective cybersecurity measures entail a multifaceted approach, encompassing robust threat detection, employee training, and proactive risk management to safeguard against evolving threats and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Google Cloud Run as a Weaponized Platform:
Exploiting the capabilities of Google Cloud Run, cyber criminals have seized upon its cost-effectiveness and efficiency, leveraging it as a potent tool for deploying distribution infrastructure. Google Cloud Run offers a seamless environment for executing diverse services and workloads, alleviating the complexities associated with managing underlying infrastructure. The adoption of Google Cloud Run in phishing campaigns signifies a notable evolution in the sophistication of threat actors, demonstrating their adeptness at exploiting legitimate cloud services for nefarious ends. This strategic utilization highlights the ingenuity of cyber criminals in leveraging emerging technologies for malicious purposes, necessitating a proactive and vigilant approach to cybersecurity. As threat actors continue to innovate and adapt, organizations must remain vigilant and implement robust security measures to mitigate the risks posed by such exploitation of cloud services. Effective defense strategies encompass a combination of advanced threat detection, access controls, and employee training to safeguard against evolving cyber threats.
Distribution Mechanism and Malware Payloads:
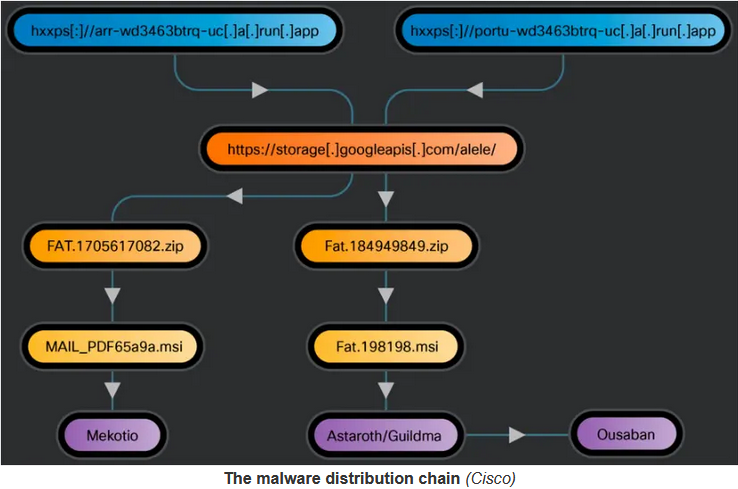
Focused primarily on Latin American and European users, the phishing campaigns adopt enticing email subjects revolving around financial documents and tax invoices to entrap unsuspecting victims. Within these deceptive emails, embedded links redirect recipients to websites hosted on the domain run[.]app. Through these websites, cyber criminals facilitate the dissemination of malicious Microsoft Installers (MSIs), which serve as gateways for the infiltration of banking trojans such as Astaroth, Mekotio, and Ousaban. These malware variants are particularly adept at infiltrating financial institutions, employing sophisticated techniques like keystroke logging and screenshot capture to monitor users’ online activities and harvest sensitive information. The orchestrated delivery of these banking trojans underscores the targeted nature of the phishing campaigns, highlighting the cybercriminals’ intent to exploit financial data and compromise user privacy for illicit gains. As such, users and organizations must remain vigilant against such threats, implementing robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against potential breaches and data theft.
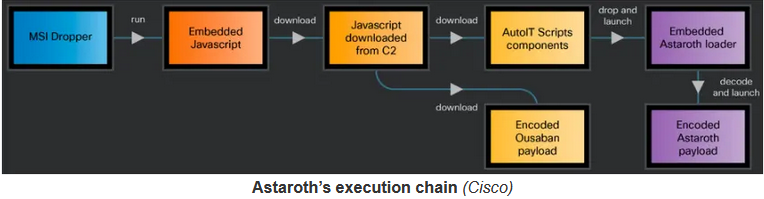
Evading Detection and Geofencing Tactics:
In an effort to circumvent detection mechanisms, threat actors resort to geofencing tactics, a method where users with IP addresses originating from the United States are redirected to seemingly legitimate websites like Google. This deceptive maneuver serves to obscure their malicious activities from security monitoring systems. Additionally, the incorporation of 302 redirects to Google Cloud Storage locations introduces another level of complexity to the distribution process, further complicating the task of cybersecurity professionals attempting to mitigate the threat. By leveraging such sophisticated techniques, cyber criminals effectively create a veil of anonymity, making it challenging for defenders to identify and neutralize malicious activities. This strategic manipulation of geolocation data and web redirection underscores the agility and adaptability of threat actors in their pursuit of evading detection. As adversaries continue to refine their tactics, cybersecurity professionals must remain vigilant and employ advanced detection and response mechanisms to effectively counter these evolving threats.
QR Code Attacks and Mobile Device Exploitation:
In a concurrent trend, cyber criminals have pivoted towards QR code attacks, reshaping their approach from targeting secure computers to exploiting vulnerabilities in users’ personal mobile devices. This strategy involves embedding malicious QR codes within phishing emails, luring unsuspecting individuals to counterfeit Microsoft Office 365 login pages. Through this deceitful method, threat actors aim to orchestrate the theft of valuable login credentials. Exploiting the comparatively lax security measures often present on mobile devices, this tactic significantly heightens the vulnerability of users to data compromise. As mobile devices increasingly serve as conduits for accessing sensitive information and conducting business transactions, the proliferation of QR code attacks poses a formidable threat to both personal and organizational security. To counter this evolving risk, users must exercise caution when scanning QR codes, verifying their authenticity before proceeding. Furthermore, organizations should implement robust security protocols, including multi-factor authentication and mobile device management solutions, to fortify defenses against such sophisticated phishing tactics.
Emerging Trends in Phishing Campaigns:
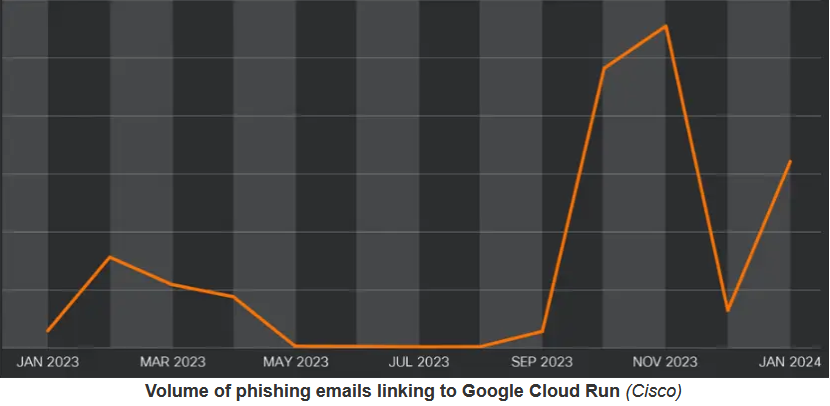
As cyber threats advance, phishing campaigns are diversifying, now extending their reach to critical sectors like oil and gas. These attacks employ intricate strategies, such as the use of sophisticated information stealers like Rhadamanthys, to infiltrate organizations. Leveraging social engineering tactics, cyber criminals exploit the trust associated with legitimate domains such as Google Maps and GitHub to deceive unsuspecting victims. Once compromised, these platforms serve as conduits for the delivery of malicious payloads, facilitating the extraction of sensitive data. The intricacy of these campaigns underscores the need for heightened vigilance and robust cybersecurity measures within the oil and gas industry. Organizations must prioritize employee awareness and training to recognize and mitigate evolving phishing threats effectively. Additionally, implementing advanced threat detection mechanisms and access controls can fortify defenses against sophisticated attacks targeting critical infrastructure. By remaining proactive and adaptive, organizations can safeguard their operations and data against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Remediation Steps:
- Implement robust access controls and monitoring mechanisms within Google Cloud environments to detect unauthorized usage of Cloud Run services.
- Regularly audit and review permissions assigned to Cloud Run instances, restricting access to trusted entities only.
- Utilize threat intelligence feeds to identify known malicious domains and IPs associated with phishing campaigns, enabling proactive blocking at the network perimeter.
- Implement geo-blocking measures to restrict access from high-risk regions known for hosting malicious activities, mitigating the impact of geofencing tactics employed by threat actors.
- Deploy advanced email security solutions capable of detecting and blocking phishing emails containing malicious QR codes, leveraging machine learning and threat intelligence for accurate detection.
- Educate employees about the risks associated with QR code attacks and provide guidance on verifying the authenticity of QR codes before scanning, emphasizing the importance of skepticism and caution.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on all critical accounts and services, including cloud platforms and email accounts, to prevent unauthorized access in case of credential theft.
- Conduct regular security awareness training sessions to educate employees about evolving phishing techniques and encourage reporting of suspicious emails or activities to the IT security team for further investigation.



