TimbreStealer Malware Spreads Through Tax-themed Phishing Scam, Targeting IT Users
Over the past few months, cybersecurity experts at Cisco Talos have brought to light a worrisome trend specifically aimed at Mexican users: an uptick in tax-themed phishing attacks that serve as a disguise for a newly discovered Windows malware called TimbreStealer. This malicious software, first identified in November 2023, represents a significant leap in sophistication, reflecting the evolving strategies employed by threat actors in the realm of cybersecurity. The intricacy of TimbreStealer’s design and its strategic deployment underscore the increasing complexity and adaptability of cyber threats in today’s landscape. This discovery serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing arms race between cybercriminals and cybersecurity professionals, wherein adversaries continuously refine their tactics to circumvent detection and infiltrate systems. The emergence of TimbreStealer underscores the critical importance of proactive threat intelligence and robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against evolving threats.
Tactical Analysis:
The developers behind TimbreStealer exhibit a sophisticated grasp of cybersecurity evasion tactics, showcasing their expertise through advanced obfuscation techniques. Notably, they employ geofencing to meticulously target users located in Mexico, ensuring the malware operates discreetly by presenting harmless files to those accessing it from regions outside of the target area. Furthermore, TimbreStealer employs custom loaders and direct system calls, strategically bypassing conventional API monitoring measures. This sophisticated approach extends to the utilization of innovative methods such as executing 64-bit code within a 32-bit process using Heaven’s Gate, showcasing the creators’ adeptness at circumventing traditional security protocols. Such intricate tactics highlight the evolving nature of cyber threats and the continuous need for heightened vigilance and adaptive security measures in defending against them.
Technical Insights:
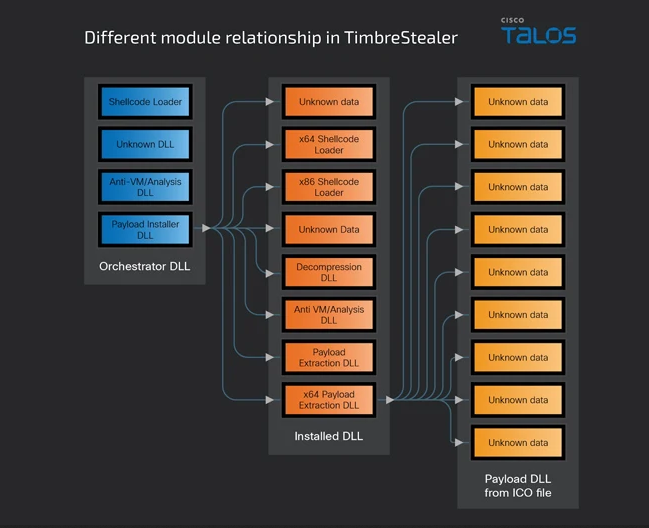
TimbreStealer boasts a sophisticated infrastructure comprising embedded modules tailored for orchestration, decryption, and self-defense mechanisms. Notably, the malware executes comprehensive checks to confirm its operation within a genuine environment, actively detecting system language and timezone configurations characteristic of Latin American regions, thus evading detection in sandbox environments. The orchestrator module meticulously examines system parameters to preempt duplicate infections, ensuring the efficiency of the payload installation process. Ultimately, this meticulous orchestration culminates in the execution of TimbreStealer’s primary functions, highlighting the malware’s strategic sophistication and its creators’ deliberate efforts to maximize infiltration while minimizing the risk of detection. Such intricate measures underscore the evolving complexity of cyber threats, emphasizing the imperative for robust cybersecurity measures to counteract these increasingly sophisticated attacks.
Payload Functionality:
The primary objective of TimbreStealer’s payload is comprehensive data harvesting, spanning various categories. This encompasses the extraction of credential information stored across multiple folders, retrieval of system metadata, logging accessed URLs, scanning for files with specific extensions indicative of sensitive data, and identifying the presence of remote desktop software, all aimed at compromising the victim’s digital footprint. In a strategic evolution, a new variant employs a Python script to maintain covert operations, as highlighted by Bitdefender researcher Andrei Lapusneanu. This variant utilizes an Apple Script block, strikingly reminiscent of the RustDoor backdoor, to clandestinely collect sensitive files from the victim’s system. Moreover, the orchestrator module diligently scrutinizes files and registry keys to verify the absence of prior infections, further ensuring the stealthy execution of TimbreStealer’s primary payload. The deployment of benign decoy files as part of the payload installation process underscores the malware’s deceptive tactics, emphasizing the meticulous orchestration of its operations to maximize infiltration and data exfiltration while minimizing the risk of detection. These intricate maneuvers underscore the escalating sophistication of cyber threats and highlight the critical need for robust cybersecurity defenses to mitigate their impact effectively.
Overlaps and Target Industries:
Cisco Talos has detected intersections between the TimbreStealer campaign and the Mispadu spam campaign noted in September 2023. However, unlike Mispadu, which predominantly aimed at the financial sector, TimbreStealer exhibits a broader scope, with its targets encompassing industries such as manufacturing and transportation. This deviation in focus suggests a strategic shift in the objectives of threat actors, reflecting a more diversified approach to data theft and cyber exploitation. While Mispadu honed in on financial institutions, TimbreStealer’s reach extends across sectors vital to critical infrastructure, potentially amplifying the magnitude of its impact. The identification of these overlaps underscores the evolving tactics employed by cybercriminals, who continually adapt their strategies to exploit vulnerabilities across various industries. As such, organizations across multiple sectors must remain vigilant and implement robust cybersecurity measures to mitigate the risks posed by multifaceted threats like TimbreStealer.
Emerging Threats:
TimbreStealer’s appearance aligns with a broader landscape of evolving malware variants, notably exemplified by the emergence of an updated version of the Atomic information stealer designed to compromise macOS systems. This underscores a trend wherein threat actors continually refine and diversify their malicious tools to target different operating systems and platforms. Concurrently, the advent of novel malware families like XSSLite serves as another testament to the dynamic and ever-changing nature of cyber threats. These developments highlight the adaptability and innovation within the realm of malicious actors, necessitating a proactive and agile cybersecurity posture to effectively counter emerging threats. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, organizations must stay abreast of these developments, implementing robust security measures to safeguard against a spectrum of potential attacks and ensuring a comprehensive defense strategy against the multifaceted challenges posed by malware variants like TimbreStealer.
Functional Capabilities:
The primary payload of TimbreStealer is engineered to harvest a diverse array of data, including credentials, system metadata, accessed URLs, and specific file types. Moreover, the malware actively seeks out remote desktop software and targets industries with a focus on manufacturing and transportation sectors, exhibiting a tailored approach to data theft.
Comparative Analysis:
Cisco Talos draws parallels between TimbreStealer and previous campaigns, particularly noting similarities with the Mispadu banking trojan observed in September 2023. While TimbreStealer showcases unique features, its emergence aligns with a broader trend of evolving information-stealing malware variants. Notably, the emergence of the Atomic variant for macOS underscores the dynamic nature of cyber threats, with adversaries constantly refining their techniques across diverse platforms.
Evasion Techniques:
The TimbreStealer phishing campaign employs sophisticated obfuscation techniques to evade detection and ensure persistence. Notably, geofencing is utilized to specifically target users in Mexico. If accessed from other locations, the payload sites return innocuous blank PDF files, thus eluding suspicion. Additionally, the malware leverages custom loaders and direct system calls to bypass conventional API monitoring, including the adoption of Heaven’s Gate to execute 64-bit code within a 32-bit process, a tactic also utilized by HijackLoader.
Embedded Modules and Checks:
TimbreStealer is equipped with a multifaceted architecture comprising embedded modules designed for orchestration, decryption, and self-defense. To evade detection, the malware conducts rigorous assessments to ascertain whether it operates within a sandbox environment, ensuring the system language is not Russian, and validating that the timezone corresponds to Latin American regions. Moreover, the orchestrator module meticulously confirms the absence of prior infections prior to initiating the payload installer component. This component ingeniously presents benign decoy files to users, masking the execution of the primary payload. These sophisticated maneuvers underscore TimbreStealer’s strategic sophistication, emphasizing its creators’ deliberate efforts to maximize infiltration while minimizing the risk of detection.
Remediation Steps:
- Educate Users: Implement comprehensive user training programs to increase awareness of phishing techniques and encourage vigilant behavior.
- Deploy Email Filtering: Utilize robust email filtering solutions to detect and block phishing emails before they reach end-users.
- Implement Geofencing Rules: Employ geofencing techniques within network security protocols to detect and prevent access from suspicious locations.
- Utilize Advanced Endpoint Protection: Deploy advanced endpoint protection solutions capable of detecting and mitigating sophisticated malware threats like TimbreStealer.
- Regular Updates and Patching: Ensure all systems and software are regularly updated with the latest security patches to address vulnerabilities exploited by malware like TimbreStealer.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Implement comprehensive network traffic monitoring to detect and block suspicious activities associated with malware communication.
- Incident Response Planning: Develop and regularly test incident response plans to efficiently mitigate and recover from potential malware infections like TimbreStealer.



