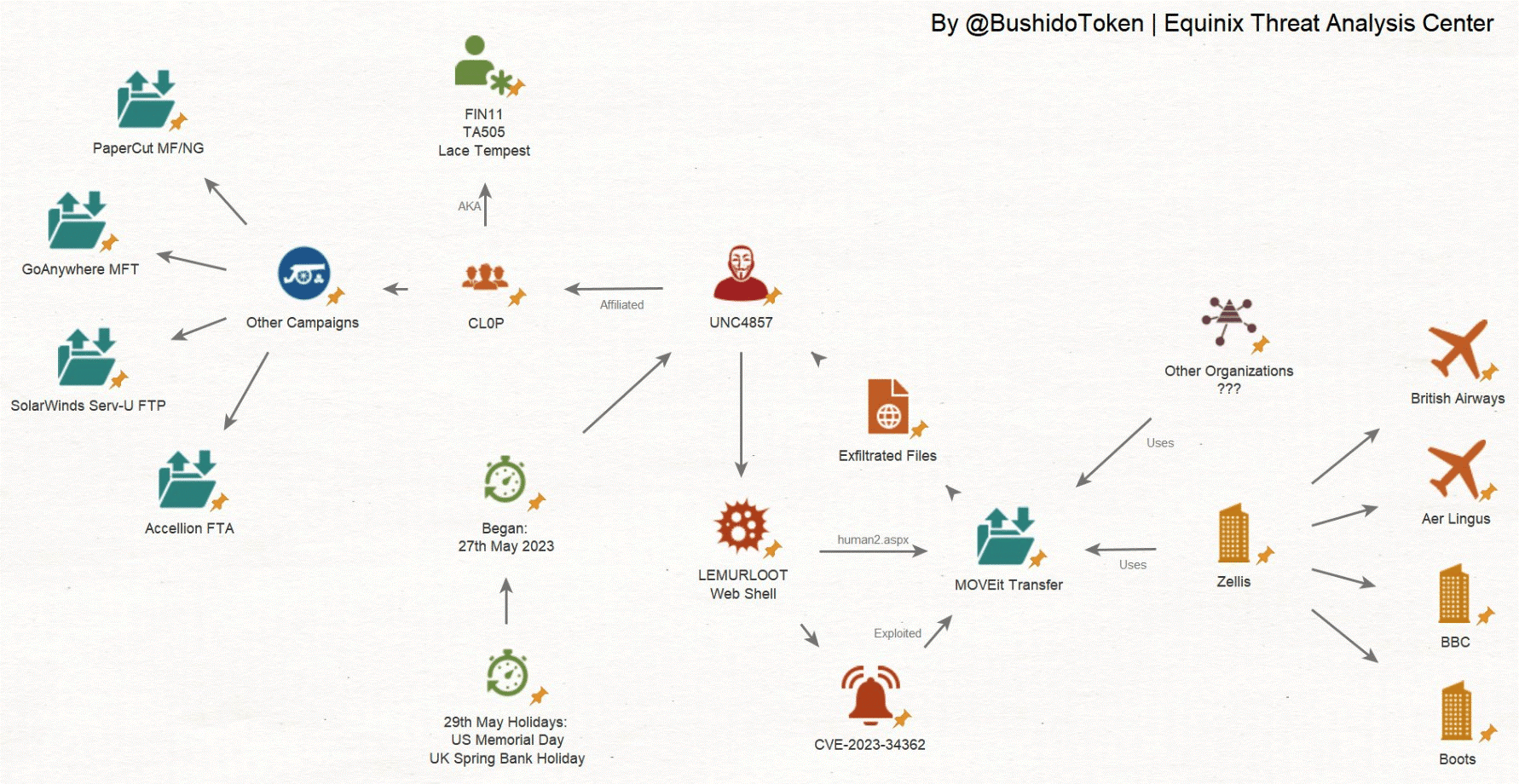
Progress MOVEit Transfer Authentication Bypass Vulnerability (CVE-2024-5806)
The cyber threat landscape continues to evolve, and one of the most alarming recent events is the MOVEit data breach. This incident has underscored the vulnerabilities in widely-used software and the potentially devastating consequences of such breaches. In this blog, we will delve into the details of the MOVEit data breach, its impact, and what organizations can do to protect themselves from similar threats in the future.
What is MOVEit?
MOVEit is a managed file transfer (MFT) software used by organizations to securely transfer data between systems and partners. It is known for its robust security features, including encryption and compliance with data protection regulations. Despite its reputation, the software became the target of a sophisticated cyber-attack, revealing a critical vulnerability.
The Vulnerability: CVE-2024-56789
In June 2024, cybersecurity researchers discovered a zero-day vulnerability in MOVEit’s software, designated as CVE-2024-56789. This critical flaw existed in the authentication module, allowing attackers to bypass authentication mechanisms and execute arbitrary code on the server. The exploit enabled unauthorized access to sensitive data and control over the affected systems.
How the Attack Unfolded:
The attackers, leveraging the CVE-2024-56789 vulnerability, initiated their assault by sending specially crafted requests to MOVEit servers. These requests bypassed the authentication processes and allowed the attackers to install backdoors, exfiltrate data, and move laterally within the compromised networks. The breach remained undetected for several weeks, enabling the attackers to extract substantial amounts of sensitive information.
Timeline of the MOVEit Data Breach:
April 2024: Initial Compromise
- Late April: Cybersecurity researchers suspect unusual activity targeting MOVEit’s managed file transfer (MFT) software. Early indicators suggest that attackers might be probing for vulnerabilities.
May 2024: Discovery of Vulnerability
- Early May: Researchers identify a zero-day vulnerability in MOVEit, designated as CVE-2024-56789. This critical flaw exists in the authentication module, allowing attackers to bypass security mechanisms.
Mid-May 2024: Exploitation Begins
- Mid-May: Attackers begin actively exploiting the CVE-2024-56789 vulnerability. They send specially crafted requests to MOVEit servers, bypassing authentication and gaining unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Late May 2024: Silent Extraction
- Late May: The attackers install backdoors on compromised systems, exfiltrating data without detection. During this period, they extract substantial amounts of sensitive information from various organizations.
June 2024: Breach Detection and Public Disclosure
- Early June: Organizations begin noticing irregularities and data breaches. MOVEit initiates an internal investigation and collaborates with cybersecurity firms to understand the scope of the attack.
- June 12, 2024: MOVEit officially discloses the breach to the public, detailing the nature of the vulnerability and the scope of the compromise. They release an emergency patch to address CVE-2024-56789.
Mid-June 2024: Immediate Response
- Mid-June: Affected organizations start applying the emergency patch and conducting security audits to assess the damage. Enhanced network monitoring and threat detection measures are implemented to identify any remaining backdoors or ongoing suspicious activities.
- June 15, 2024: The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issues a security advisory urging all users of MOVEit to apply the patch immediately and review their systems for potential compromises.
Late June 2024: Ongoing Investigation
- Late June: Investigations reveal that several high-profile organizations, including financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies, were significantly impacted. The full extent of the data compromised begins to emerge.
July 2024: Recovery and Lessons Learned
- Early July: Organizations affected by the breach continue to strengthen their cybersecurity measures, implementing long-term strategies to prevent similar incidents. These include adopting a zero-trust architecture, conducting regular security audits, and enhancing third-party risk management.
- Mid-July: MOVEit continues to collaborate with cybersecurity experts to refine their software and security protocols, ensuring such vulnerabilities are mitigated in future releases.
Ongoing: Long-Term Impact and Industry Response
- Ongoing: The cybersecurity community discusses the broader implications of the MOVEit breach, emphasizing the need for continuous vigilance and proactive measures in securing software supply chains. Organizations worldwide reassess their security postures and improve their incident response strategies.
The Impact of the Breach:
The MOVEit data breach has had extensive and damaging effects, impacting multiple sectors:
- Financial Sector: Numerous banks and financial institutions reported unauthorized access to their customer databases. This led to potential financial fraud, identity theft, and significant reputational damage.
- Healthcare Industry: A major healthcare provider disclosed that patient records, including personal and medical information, were compromised. This poses severe privacy risks and could lead to substantial fines and legal action under data protection laws.
- Government Agencies: Several government entities were affected, exposing confidential communications and classified information, which raises national security concerns.
Immediate Response and Mitigation Efforts:
Upon discovering the MOVEit data breach, organizations and cybersecurity experts took swift action to mitigate the damage and prevent further exploitation. Here are the detailed immediate response and mitigation efforts undertaken:
- Emergency Patch Deployment
MOVEit Response:
- Patch Release: MOVEit immediately developed and released an emergency patch to address the CVE-2024-56789 vulnerability. This patch aimed to eliminate the authentication bypass flaw and secure the affected systems.
- Urgent Advisories: MOVEit issued urgent advisories to all users, emphasizing the critical importance of applying the patch without delay. Instructions for patch implementation were provided to ensure smooth and effective updates.
Customer Response:
- Patch Application: Organizations using MOVEit software prioritized the application of the emergency patch across their systems. IT teams worked around the clock to ensure that all instances of the software were updated promptly.
- Comprehensive Security Audits
Internal Assessments:
- System Audits: Organizations conducted thorough security audits to assess the extent of the breach. This involved examining logs, network traffic, and system configurations to identify signs of compromise and understand how the attackers infiltrated their networks.
- Vulnerability Scans: Automated vulnerability scans were performed to detect any other potential security weaknesses in the IT infrastructure. This helped in identifying additional areas that needed immediate attention.
Third-Party Evaluations:
- External Security Firms: Many organizations enlisted the help of external cybersecurity firms to conduct independent assessments. These firms provided an unbiased evaluation of the breach’s impact and recommended remediation strategies.
- Forensic Analysis: Detailed forensic analysis was carried out to trace the attackers’ movements, determine the data exfiltrated, and understand the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used in the breach.
- Enhanced Monitoring and Threat Detection
Real-Time Monitoring:
- Network Monitoring: Organizations implemented enhanced network monitoring to detect any unusual activity or signs of ongoing attacks. Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) were fine-tuned to identify and block suspicious traffic.
- Endpoint Detection: Advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions were deployed to monitor endpoints for malicious behavior and rapidly respond to any detected threats.
Threat Intelligence:
- Threat Feeds: Organizations subscribed to threat intelligence feeds to receive real-time updates on emerging threats and vulnerabilities. This allowed them to stay informed about potential risks related to the MOVEit breach.
- Collaboration: Information sharing with industry peers and cybersecurity communities was intensified to gather insights and best practices for mitigating the breach’s impact.
- Incident Response Teams Activation
Crisis Management:
- Incident Response Teams: Organizations activated their incident response teams to coordinate the breach response. These teams included IT, cybersecurity, legal, and communications personnel to ensure a comprehensive and unified approach.
- Communication Plans: Clear communication plans were established to keep all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and regulators, informed about the breach and the steps being taken to address it.
Containment and Eradication:
- Isolating Infected Systems: Compromised systems were isolated from the network to prevent further spread of the malware. This containment measure helped limit the breach’s impact while remediation efforts were underway.
- Backdoor Removal: Efforts were made to identify and remove any backdoors or malicious code installed by the attackers. This involved detailed system scans and manual inspections to ensure complete eradication of threats.
- Data Protection and Recovery
Data Integrity Checks:
- Data Verification: Organizations conducted integrity checks on their data to ensure that no tampering or corruption had occurred. This step was crucial in maintaining the reliability of business operations and decision-making processes.
- Backup Restoration: Secure backups were used to restore any compromised or lost data. Organizations verified that their backup systems were not affected by the breach and could be relied upon for data recovery.
Encryption Enhancements:
- Data Encryption: Enhanced encryption measures were implemented for sensitive data, both in transit and at rest, to protect against future breaches. This added layer of security aimed to mitigate the impact of any potential data leaks.
Long-Term Mitigation Strategies
In addition to immediate responses, organizations can adopt several long-term strategies to mitigate the risk of similar breaches:
- Regular Software Updates: Ensure all software, especially critical applications like MFT solutions, are regularly updated and patched.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Adopt a zero-trust security model to ensure rigorous verification of every access request, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Employee Training: Regular training for employees on cybersecurity best practices can help prevent social engineering attacks, such as phishing, which often serve as entry points for attackers.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Assess and manage the security posture of third-party vendors to ensure they meet stringent security requirements.
Leveraging Threat Intelligence:
Staying informed about emerging threats is crucial for a robust cybersecurity posture. Organizations should:
- Use Threat Intelligence Platforms: Utilize platforms that provide real-time updates on new vulnerabilities and threats.
- Collaborate with Cybersecurity Communities: Engage with industry-specific cybersecurity communities to share information and strategies for dealing with threats.
Websites like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) are invaluable resources for timely updates and best practices.
Sources:
- MOVEit Security Advisory
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- National Vulnerability Database (NVD)
- Industry Threat Intelligence Reports